

Now Available!
Get your copy of the 7th Annual State of Smart Manufacturing and hear from 300+ manufacturers in this new survey report!
Subscribe to Our Blog
For a monthly digest of expert insights, data points, and tips like the ones in this article.
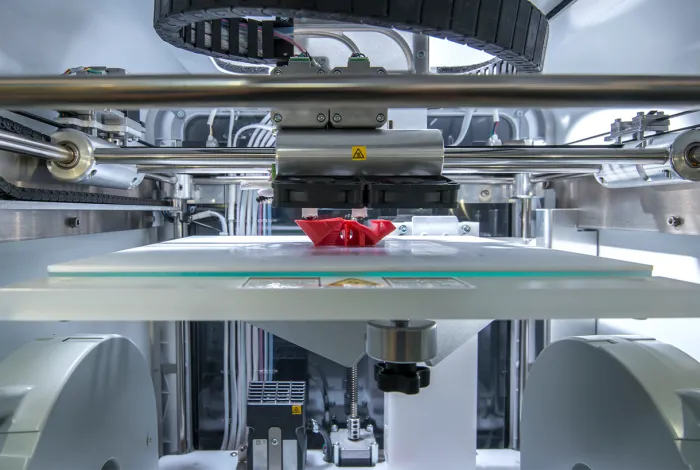
Additive manufacturing (AM) is the industrial production name for 3D printing. Using computer aided design (CAD) or 3D object scanners, additive manufacturing allows for the creation of three-dimensional objects by depositing materials, usually in layers. As production continues to grow and additive manufacturing industrializes, manufacturers require effective strategies to help them manage their additive manufacturing workflows. Additive manufacturing execution systems (MES) use workflow software to enable greater traceability, provide insights, and help establish best practice processes. In this guide, we will discuss additive MES in detail, covering the key benefits and how to recognize if it’s the right time for your company to invest in this software.
What Is an Additive Manufacturing Execution System?
In competitive industries, manufacturers are under pressure to manufacture high-quality products at speed – without huge costs. As a result, companies are always looking to implement lean processes and new technology to help them meet these manufacturing demands. A recent report by EY states that 46% of companies plan to adopt additive manufacturing for end-part production by 2022. Additive manufacturing is seen as a way of producing products more efficiently and more cost-effectively, but for it to work at its maximum potential, manufacturers use additive manufacturing execution systems to assist with production visibility, resource management, enable proactive decision making, and optimize planning and scheduling.
Manufacturing execution systems perform the same functions in traditional manufacturing. This technology increases uptime, reduces inventory, and helps management improve the efficiency of the entire production cycle, from the shop floor through to manufacturing. This software is highly effective, but isn’t suited to the unique requirements of additive manufacturing execution systems. This is because additive manufacturing has a different approach to design, production, and process management, with the steps needed to manage post-processing operations and conduct quality assurance drastically differing from traditional manufacturing. These differences make it important for businesses to understand the unique benefits of deploying additive MES software, helping them recognize if their manufacturing processes could greatly benefit from this technology.
7 Key Benefits of Additive Manufacturing Execution Systems
Additive manufacturing execution systems are designed to ensure production teams get the best out of the software they use in production. Understanding the key benefits in more detail will help manufacturers build a business case for this technology.
1. Optimization of resources
Additive MES software uses inbuilt algorithms to process orders and assign print jobs to machines. These functions are performed based on data collected on job priority, machine availability, order date, material availability, and print bed size. This makes it far more accurate than human calculations and ensures more efficient use of resources. Additive MES software also ensures jobs are completed using the least possible power, materials, and human effort – saving businesses money.
2. Efficient, automated workflows
Additive MES replaces spreadsheets and manual processes with streamlined, digital workflows. When additive manufacturing operations expand, using manual processes for data collection and scheduling can lead to bottlenecks. Human error and lack of visibility can limit the capabilities of the software. Additive MES automates and links manual processes on a digitalized platform, reducing manual labor and improving efficiency.
3. Full traceability
Additive manufacturing execution systems can create a record of the journey of a product from raw material to finished article. This can be used to improve the overall efficiency of the production process and is useful for customers looking for a picture of the lifecycle of the product their purchasing.
4. Delay prediction
Additive MES monitors real-time machine data and tracks schedule times, estimating future lead times. Using this data, the software can predict and inform customers of potential delays. This reduces the need for dialogue between the two parties via calls or emails.
5. Reduces operational costs
The automation and streamlined workflow provided by additive MES helps companies reduce operational costs. Automation reduces labor costs and allows the human workforce to prioritize high-value tasks. Using data to schedule work and order materials also saves money on wasted resources, controlling costs, and optimizing production.
6. Connection and standardization
An additive manufacturing execution system helps facilitate communication between disparate elements of production processes. The software connects processes like order management, machine management, and post-processing, ensuring smooth communication between each manufacturing stage. Connecting all your processes under one piece of software helps users manage production and saves them from moving information manually between the different stages.
7. Scalability
Using additive MES software is essential for growth. As an organization’s additive manufacturing production increases, they will need workflow software to help accommodate the growth and respond to the evolving needs of the business. Deploying additive MES will easily enable organizations to accommodate fast growth and increased production volumes.

