The MES Beginners Guide
A 101 guide outlining the features, functions and benefits of a Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES).
Download the PDF
What is a Manufacturing Execution System (MES)?
A Manufacturing Execution System (MES) helps businesses ensure that their manufacturing operations and production work efficiently. The software system connects, monitors, and controls machines, work centers, and data flows on the factory floor. The MES does this by tracking and gathering real-time data throughout the production lifecycle and on every piece of equipment involved in the production process—from order to delivery.
An MES provides businesses with data on product tracking and genealogy, performance, traceability, management, work in progress (WIP), and other plant activities throughout the production cycle. This information provides decision-makers with detailed insight on how to optimize their operations.
On this page, we’ll cover manufacturing execution systems in detail and provide links to other resources on our website, helping you understand how this technology can create efficiency in your plant.
What Does a Manufacturing Execution System Do?
The Manufacturing Enterprise Solutions Associations (MESA) is an organization that monitors the effective application of IT to help improve operations management. The MESA-11 model indicates there are 11 core functions of an MES.
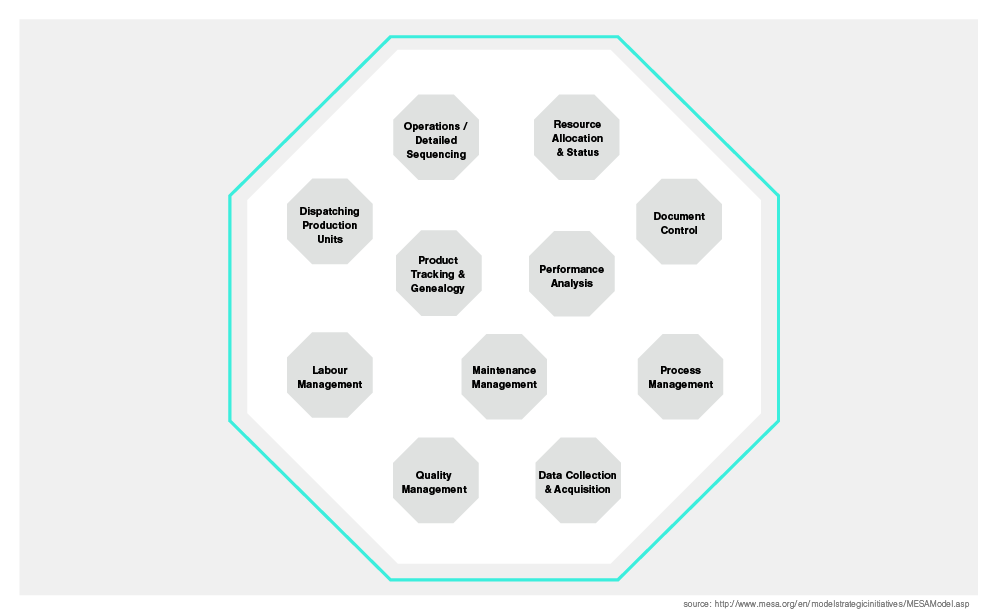
We’ll break each one down in a little more detail so you understand exactly what you can expect from an MES.
- Operations management – provides employees with a global view of planned production orders and their production routing.
- Resource allocation – defines and tracks the status of your resources and how they’re being used in manufacturing.
- Dispatching production unit – manages real-time production data flow between the enterprise resource planning (ERP) and the factory floor.
- Performance analysis – uses data to calculate key performance indicators (KPIs) like reword, scrap, process, capability, OEE, and more.
- Maintenance management – helps accurately plan preventative machine maintenance to reduce downtime.
- Process management – provides process routing and operational sequencing.
- Quality management – assesses the quality of your manufacturing process and equipment, including deviations and exceptions.
- Data collection/acquisition – gathers and recovers essential data when required.
- Product tracking and genealogy – groups final parts or batches with the corresponding manufacturing data, from raw materials through to component assembly.
- Labor management – ensures people, products and operations are in the correct place in the manufacturing process to maximize efficiency.
- Document control – provides a simple way for operators to access important documents such as instructions, drawings, and notes.
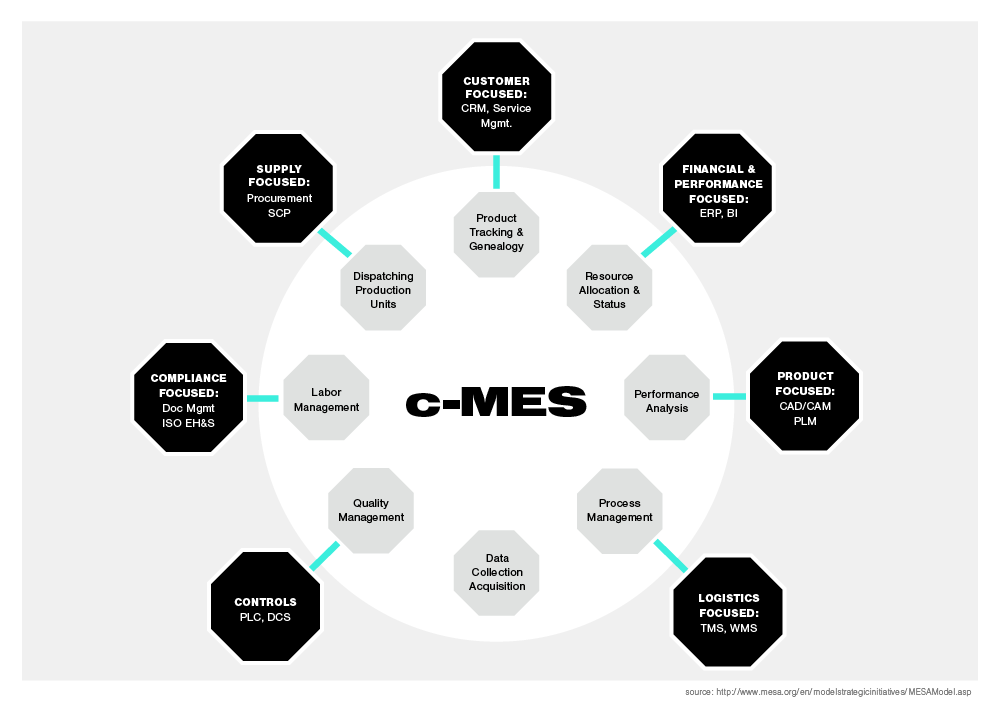
In 2004, the MESA model was expanded to include business operations. The model shows how the core operations in the original interact with business operations, taking into account competition, outsourcing and asset optimization. This update is known as Collaborative MES or C-MES. The purpose was to create a link between MES and other business operation areas, including supply focused systems, customer focused systems such as CRM, performance focused systems such as ERP and BI software.
In 2008, the model was expanded to its current version. This model covers enterprise-level strategic initiatives, business operations, plant operations and actual production, creating a link between the different levels and disciplines within manufacturing and production and providing a platform for mutual understanding and planning for improved performance.
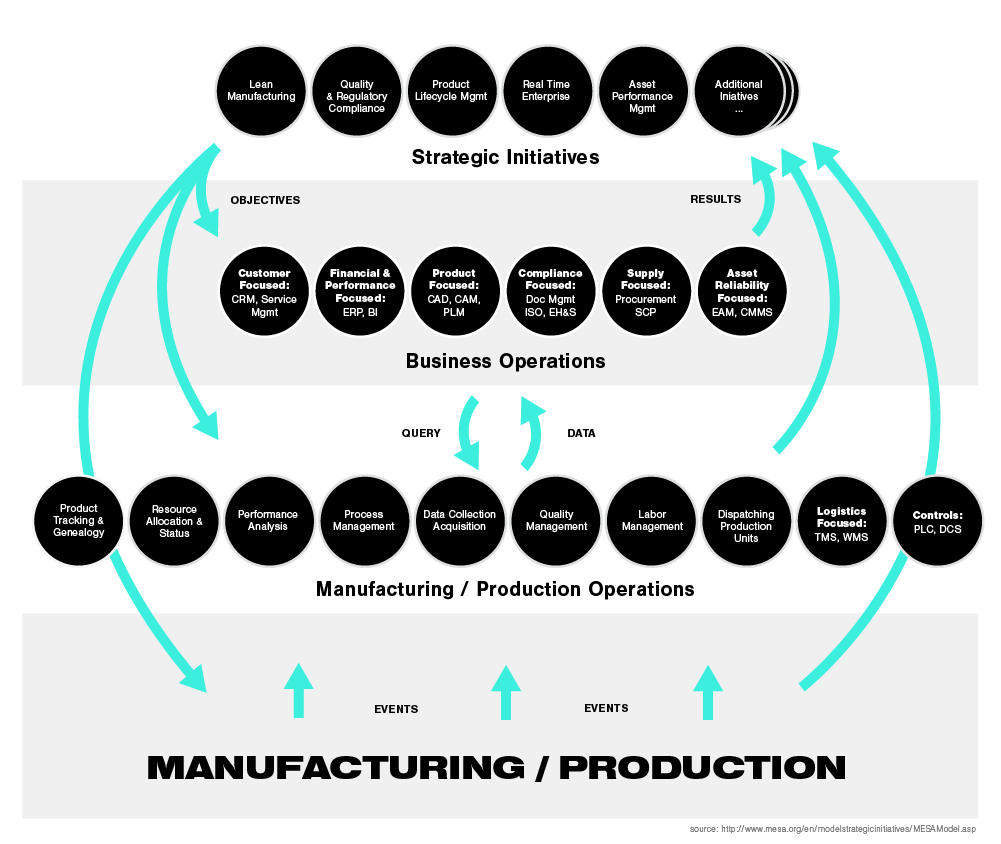
Originally, in order for a system to be considered an MES, it must have all of the functional groups included in the model. This new model acts as an intermediary between automation and corporate management, it is an integration hub for information throughout a corporation.
Manufacturing Execution System Architecture
The ANSI/ISA-95 are an international standard for the integration of enterprise and control systems. The ANSI/ISA-95 merged the MESA-11 model with the Purdue Reference Model to create a functional hierarchy for MES. As you can see on the infographic below, MES was established at intermediate level three, falling between ERP and process control.
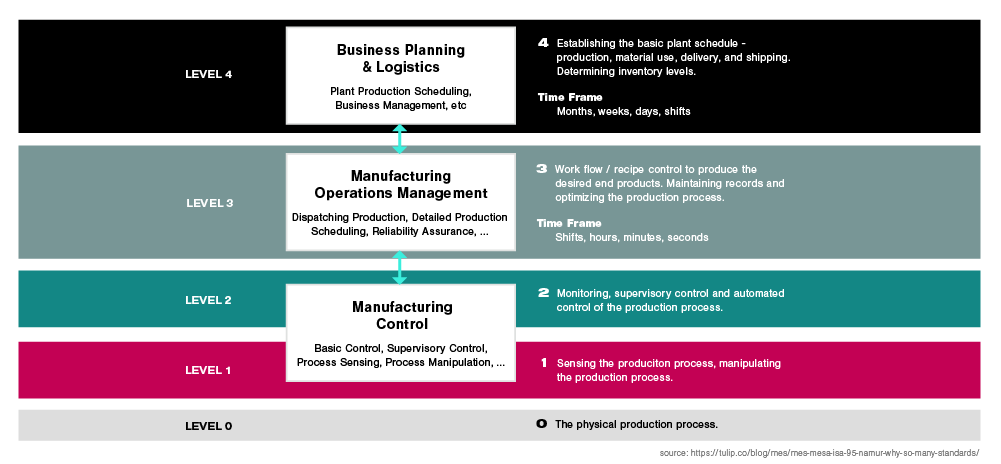
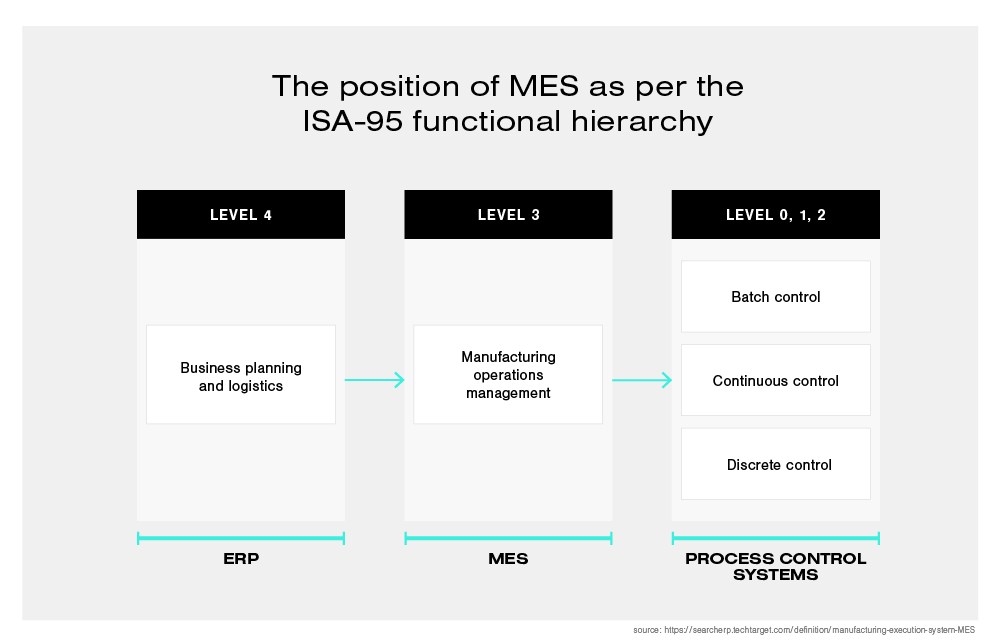
MES is a functional layer between business planning and logistics and the process control systems in manufacturing. Using real-time workflow visibility, flexibility and the insights provided by this technology will help decision-makers improve the efficiency and quality on factory floors.
MES is also important in industries where businesses are required to meet regulatory compliance set by the Food and Drug Administration for regulated products. Good examples of industries that will benefit from an MES are pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, medical device class and biotechnology.
What are the Benefits of Using a Manufacturing Execution System?
If you’re considering an MES, knowing all the benefits it will bring your business is important. Here are some examples of how an MES will benefit your manufacturing efficiency:
- Improved customer satisfaction
- Improved regulatory compliance
- Improved machine efficiency
- Improved supply chain visibility
- Improved product quality
- Proves full control over your manufacturing process
- Faster time to market
- Eliminated paperwork and manual data entry
- Lower labor costs
- Accelerates trace analysis
- Reduced order lead time
- Reduced WIP inventory
- Reduced manufacturing time
All of these contribute to a more efficient workforce, increased quality, and a higher profitability, three advantages all businesses are looking to gain over a competitive market. There are also different types of MES available, including cloud-based services, so it’s worth researching in more detail and finding out what technology is the best fit for your company.
Is an MES Right for My Business?
We’ve covered the benefits of using a manufacturing execution system, but how do you know it’s the right fit for your business? MES technology will undoubtedly improve your workflow, productivity, and overall quality on the factory floor, but it’s still an investment. Smaller manufacturers may find their production operations or profit margins simply aren’t large enough to justify installing this type of software. You need to look at your manufacturing and production cycle and decide if an MES will make a noticeable difference.
-
Automotive
Improves quality through real-time insights
A multi-billion dollar, Tier 1 supplier to the automotive industry found it challenging to gain real insights into business performance, quality, capacity planning, and how to get real-time understanding of financial status.
With the help of MES technology, they experienced a 5% increase in manufacturing output, and an improvement in inventory turns of 5-10% with a positive impact on cash flow.
-
Food and Beverage-Quality
Improves Quality and Regulatory Compliance
The food and beverage industry is experiencing monumental changes with the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) to give the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) greater authority over how food, both human and animal, is grown. In all these standards, increased accountability is being passed on to manufacturing suppliers.
Integrating MES, ERP on other complementary systems allows manufacturers to ensure process quality and more effective, efficient production. It also provides real-time data on the entire production process, providing electronic recording and full disclosure over how a plant is run. -
Food and Beverage-Operational Excellence
Achieves Operational Excellence
A food and beverage company that supplies the fast food industry faced challenges such as paper-based processes causing issues, limited real-time visibility and inconsistent reporting, not being able to track inventory cost from receipt to finished product and poor ingredient tracking and traceability.
With the help of MES technology, their inventory accuracy rose to 99.6% compared to 70% in 2015. They achieved easy compliance with customer score cards, demonstrating the ability to be a strategic business partner. Finally, they could better determine the ingredients needed the produce their product, improving efficiency and quality.
Certain industries will benefit further from an MES. The material traceability makes MES technology invaluable to manufacturers who must adhere to strict regulations. This includes food and beverage, medical devices, aeronautics, aerospace, and defense industries. If your business falls into one of those sectors, you should consider the improvements brought by installing an MES.
What’s the Difference Between an MES and ERP System?
We covered earlier how MES is an essential layer between ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) and the process control systems in manufacturing. MES and ERP play separate roles but work together to improve the manufacturing process. ERP systems integrate different parts of an organization into one information system. All the data is available in real-time, helping decision-makers make more informed business decisions, just like an MES does. Both systems work to help simplify the decision-making process for business owners and management, presenting them with the real-time data they need to assess how the company is performing.
MES performs a similar role but for the layer between your manufacturing and business, planning and logistic systems, or ERP. ERP systems show you that you might need to make improvements to your production cycle, MES tells you how. The integration of ERP and MES is fundamental to Industry 4.0, which is believed to be the future of operational efficiency. Using the two together helps businesses become more flexible and responsive to changing demands.
If you’re interested in learning more about Plex MES technology and how it can benefit your business, you can learn more about our products here.
Still looking for more information on manufacturing execution systems? You can find additional resources below.
Did You Know?
With a PLEX MES you can expect:
- Paperless, easy-to-use Control Panel.
- Automated tasks to prevent human errors and increase productivity.
- Mitigated compliance risk through database-driven traceability and direct, in-line quality control.
- A single source of truth to real time data between your top-floor and shop-floor.
- Cloud access from anywhere, at any time, on any connected device.
- Connectivity with your manufacturing ERP.
- Full tracking of every action on the shop floor.

With a traditional manual system you get:
- Pervasive manual processes.
- Excel or paper-based collection of production and scrap data.
- Delayed or incorrect business data.
- Disparate, disconnected stand-alone applications.
- Long lag times in addressing quality issues on the plant floor.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What does MES stand for?
MES stands for Manufacturing Execution System. An MES system is used to track real-time data on the production cycle.
-
Is SAP an MES system?
SAP Manufacturing Execution (SAP ME) is a comprehensive manufacturing execution system (MES) used for discrete manufacturing processes. It is used to manage, monitor, and automate operations on the production line.
-
Who uses MES software?
Manufacturing Execution Systems are mostly used by production managers, shop floor supervisors, and any employees involved in the production process.





